- Overview
-
Michelangelo was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect and poet of the High Renaissance born in the Republic of Florence, who exerted an unparalleled influence on the development of Western art. Considered by some the greatest living artist during his lifetime, he has since been described as one of the greatest artists of all time. Despite making few forays beyond the arts, his artistic versatility was of such a high order that he is often considered a contender for the title of the archetypal Renaissance man, along with his rival, the fellow Florentine and client of the Medici, Leonardo da Vinci.
- Career
-
- Impressed by the quality of his design, Cardinal Raffaele Riario invited him to Rome and commissioned him to work on a statue of the Roman wine god Bacchus.
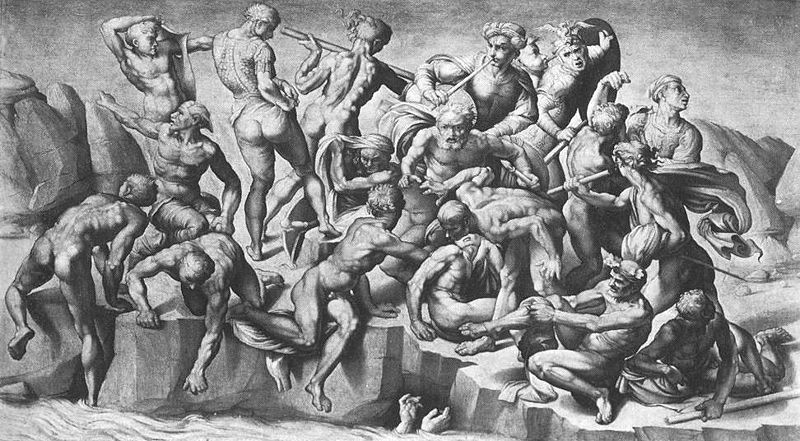
- In 1499, he returned to Florence again but this time as an art star. He was recognized as the most talented sculptor of Italy and was commissioned to carve a statue of ‘David’. He turned a huge piece of marble into a dominating figure which was placed on the gable of Florence Cathedral.
- In 1508, Julius commissioned him to decorate the ceiling of Sistine Chapel, a project which took about four years to complete. After the ceiling was completed in 1512, Michelangelo continued to work on the tomb of Julius II for the next several decades.
- During this time, he also designed the Medici Chapel in Florence and the historical Laurentian Library at San Lorenzo's Church, Florence. In 1534 he finally settled in Rome and later on met Vittoria Colonna who became the subject and recipient of many of his more than 300 poems and sonnets.
- In 1546, he was appointed the chief architect of St. Peter’s Basilica, Rome, and devoted himself entirely to architecture and poetry during his later years.
- Impressed by the quality of his design, Cardinal Raffaele Riario invited him to Rome and commissioned him to work on a statue of the Roman wine god Bacchus.
- On View
-
- The Louvre, Paris
- Rijksmuseum, Amsterdam
- National Gallery, London
- British Museum, London
- Isabella Stewart Gardener Museum, Boston
- Kimbell Art Museum, Fort Worth
- Palazzo Vecchio, Florence
- Royal Collection Trust
- Uffizi Gallery, Florence